V. Principality of Monaco






Principality of Monaco — Andrew Miller
Officially known as the Principality of Monaco, the city-state holds the record as the most densely populated and also the second smallest sovereign state in the world. Located on the French Riviera, the city-state is set along the Mediterranean Sea and surrounded by France. Due to its status as a tax haven, Monaco is known to be the most expensive and the wealthiest place in the world.


Population: 38,682 people people
Area: 2.020 square km2
Population Density: 19,009 people/km2
Politics:
Monaco is a principality governed under a form of constitutional monarchy, with the Sovereign Prince of Monaco as head of state. The prince shares his veto power with the unicameral National Council. The 24 members of the National Council are elected for five-year terms; 16 are chosen through a majority electoral system and 8 by proportional
representation. There is no geographical distinction between the State and City of Monaco, although the responsibilities of the government (state-level) and of the municipality (city-level) are different.
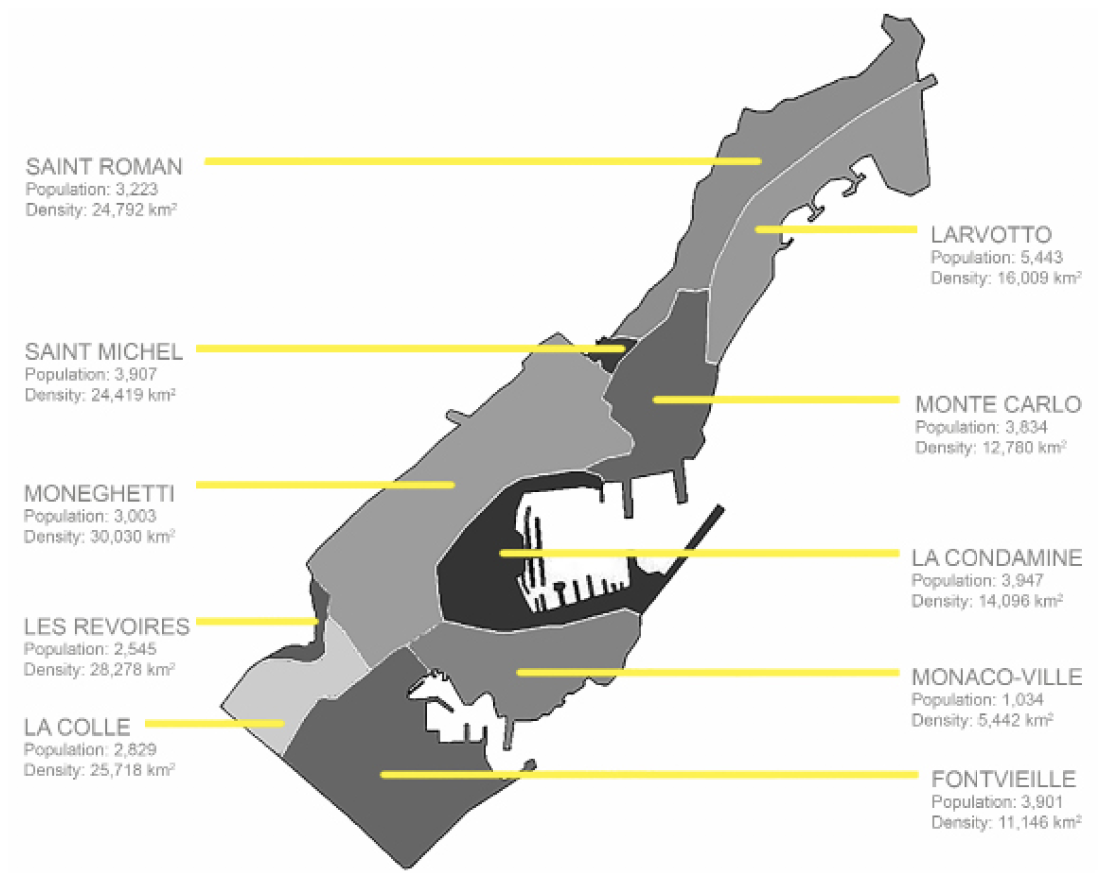
The principality is divided into ten municipalities: Monaco-Ville, Monte Carlo, La Condamine, Fontvieille, Moneghetti, Larvotto, La Rousse/ Saint Roman, Saint Michel, La Colle, Les Revoires.

IMPRESSIONS OF HIGH DENSITY; DENSITYGRADIENT, AND PHYSICAL DENSITY.
.
Land Scarcity within the Principality, the wealth of its citizens, and the Limited Taxes creates a hyper-competitive real estate market. Due to this, Monaco Has Extremely High Physical Density with limited Density Gradient until the Border with France. Interestingly, Monaco has relatively low occupancy density compared to other high dense.
cities, due in large part of the wealth of its citizens.

Principality of Monaco. High Density Buildig Typologies

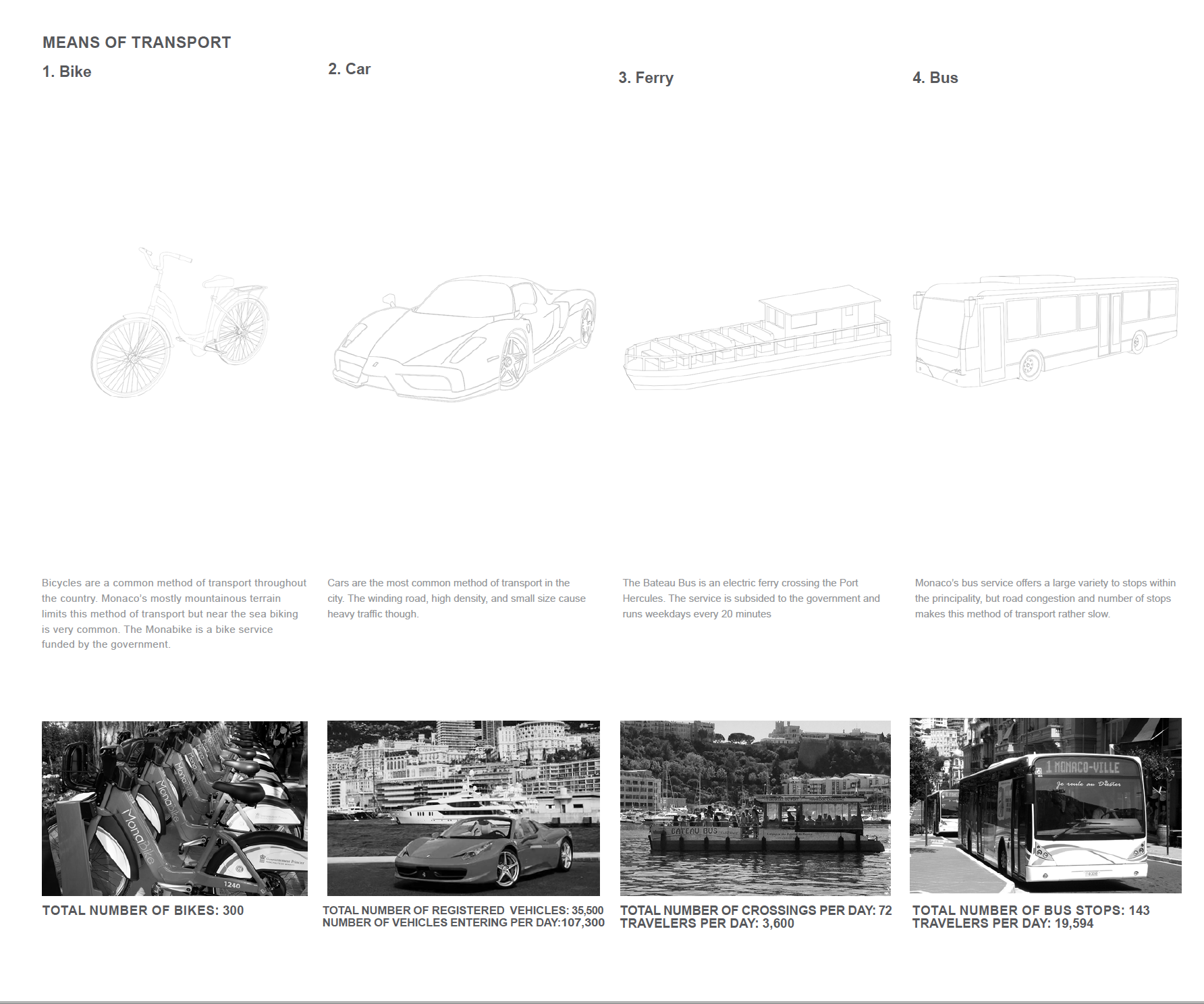
Principality of Monaco. Means of transportation

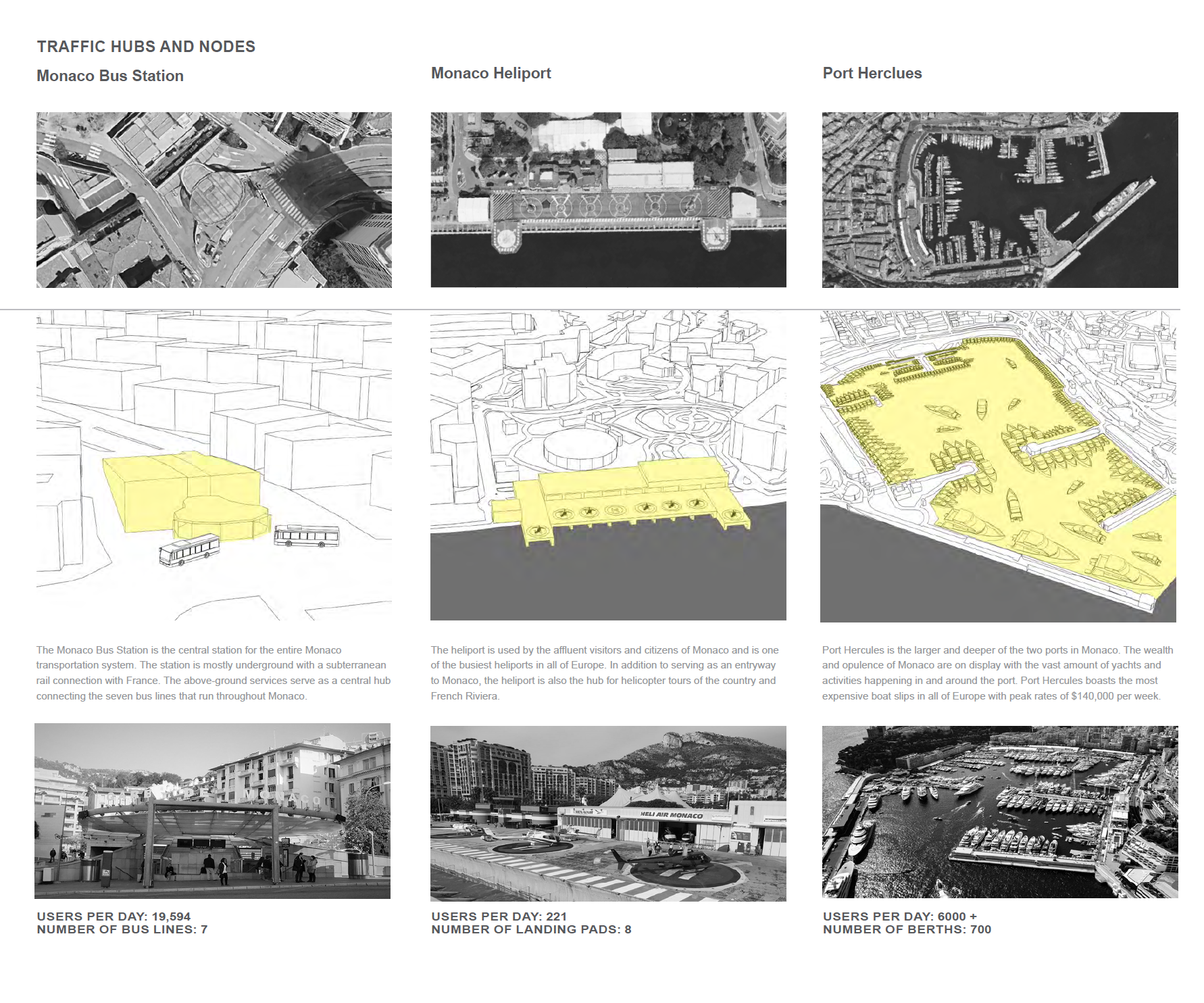
Principality of Monaco. Traffic hubs and nodes
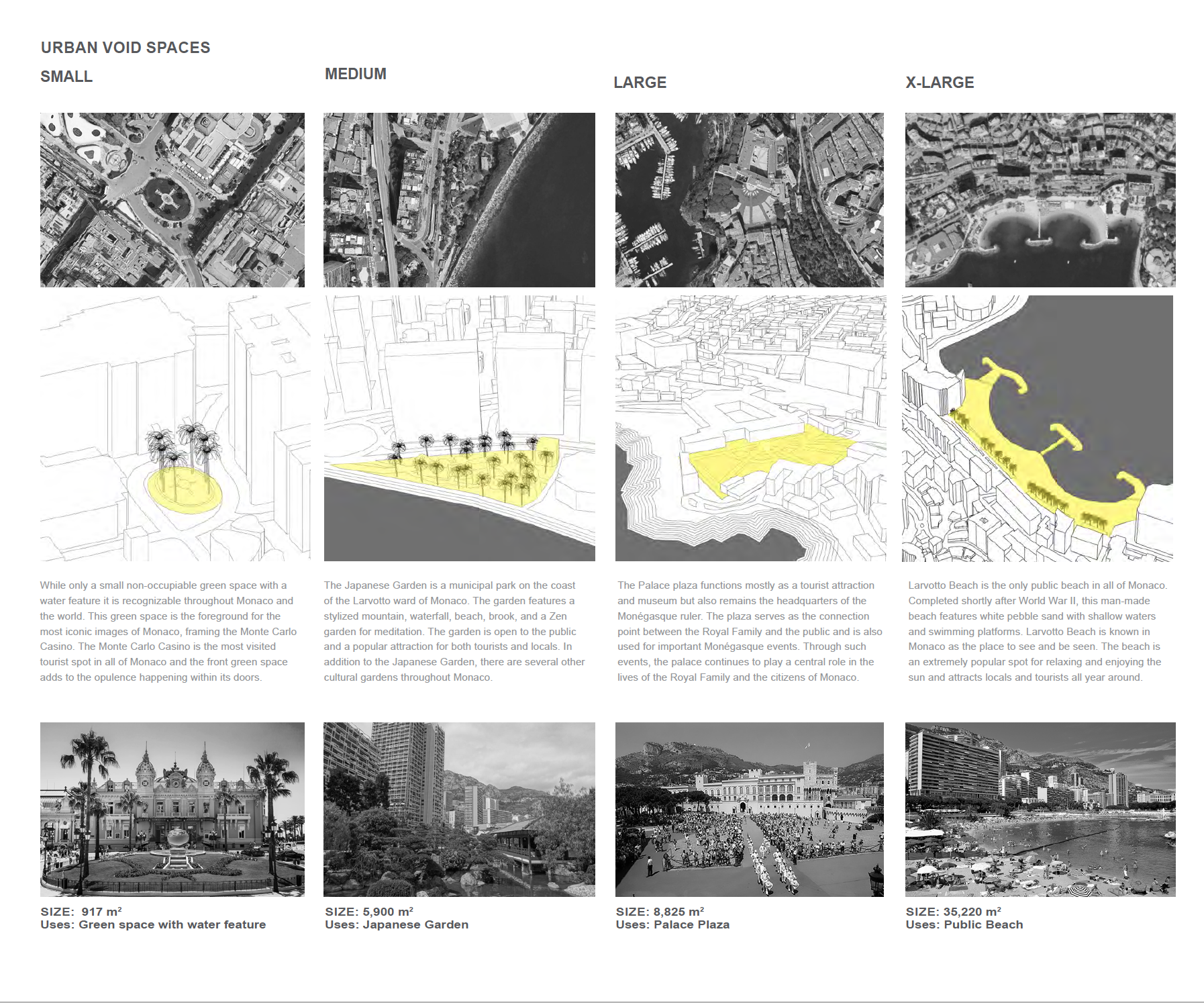
 Principality of Monaco. Urban Void Spaces
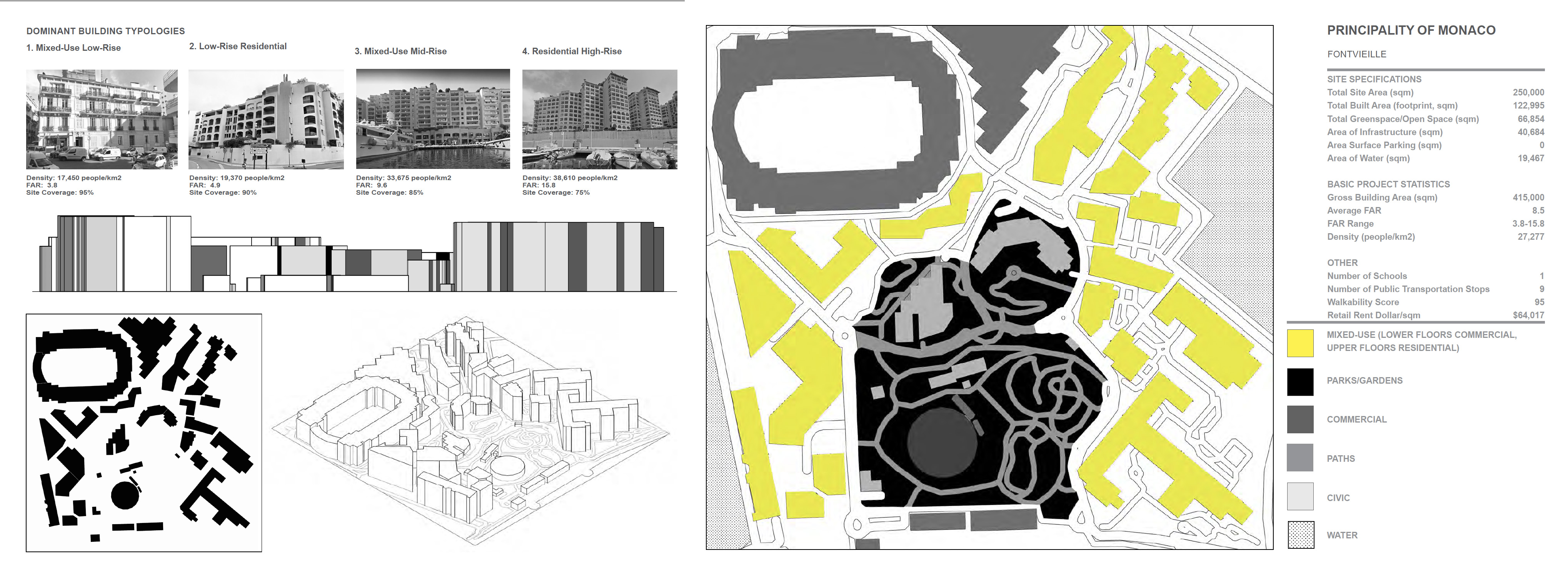
Principality of Monaco. Urban Void SpacesPrincipality of Monaco- Fontvieille Neighborhood:
Area: 0.35 square km
Population: 3,901 people
Population Density: 11,146 people/km2

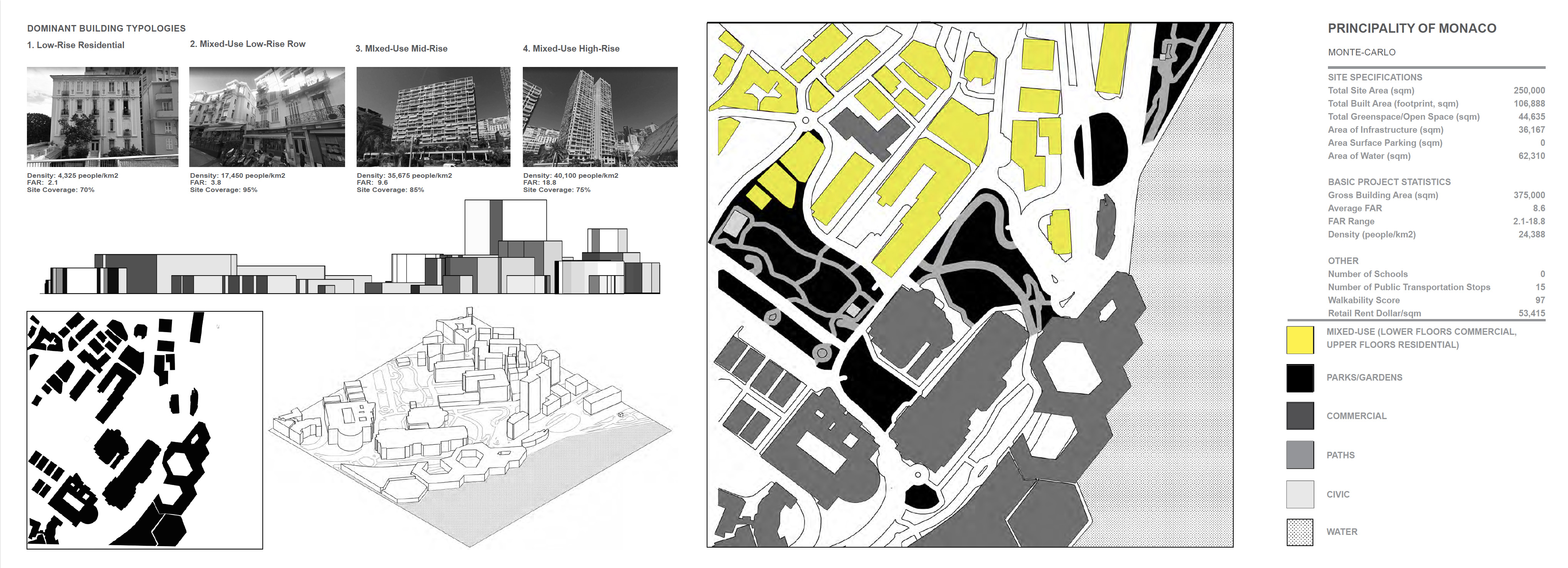
Principality of Monaco- Monte Carlo:
Area: 0.3 square km
Population: 3,834 people
Population Density: 12,780 people/km2

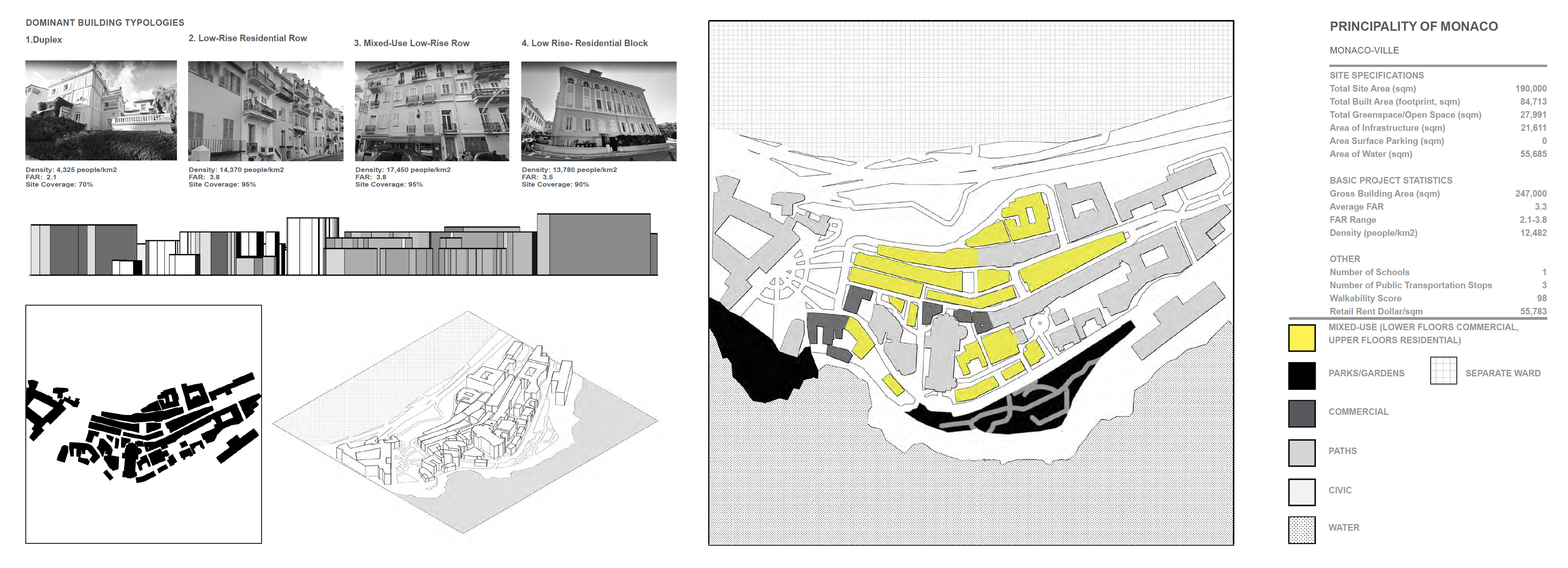
Principality of Monaco- Monaco-Ville:
Area: 0.19 square km
Population: 1,034 people
Population Density: 5,442 people/km2

_____________________________________________________________________________________
CITY CENTER: PORTIER COVE, Monaco
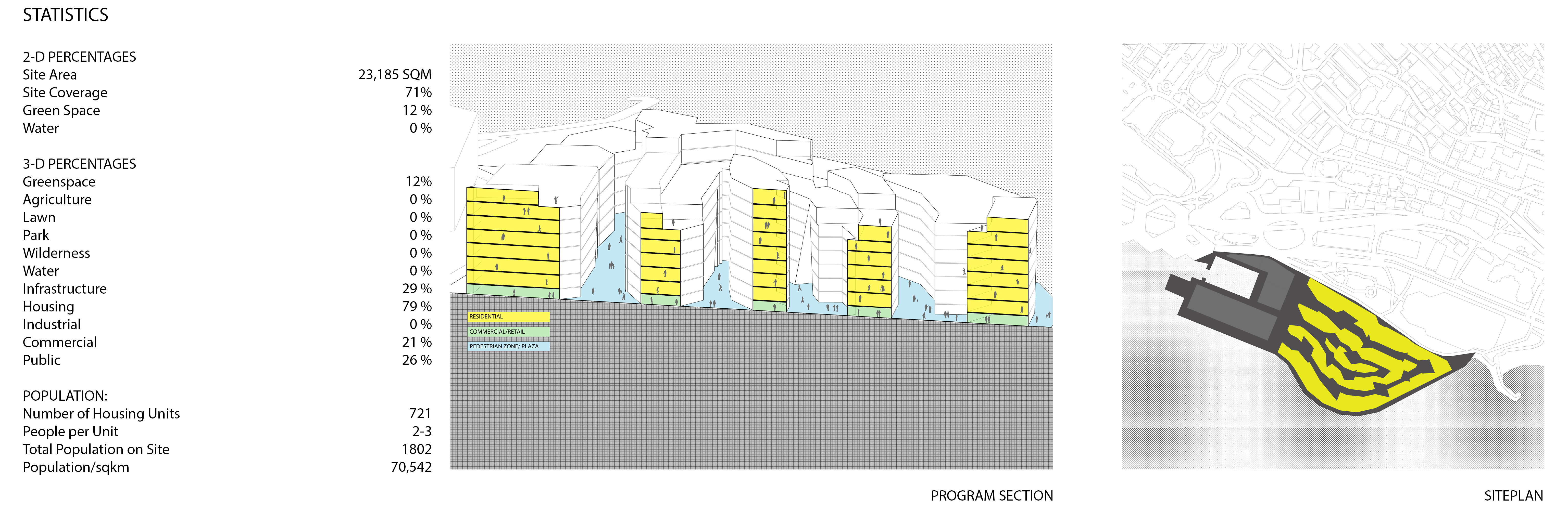
City Center: Portier Cove is a proposal that looks to expand upon the historic city center typology found across Europe. The site of the proposal is an ongoing land reclamation project happening off the coast between the Monte-Carlo and Larvotto districts of Monaco. The City Center: Portier Cove proposal is a response to the planned construction on the site, which does not adequately respond to the housing crisis in Monaco. With land scarcity and the most expensive housing market in the world, reimagining the planned low-density villas with a more practical high-density solution offers some much-needed relief to the Monaco housing crisis.
Pulling from the historic city centers across Europe and within Monaco itself, the proposal takes advantage of a proven technique for creating high-density while also retaining the human scale and livability. Creating a mixed-use space modeled after the historic city centers, the proposal creates a pedestrian-only zone with commercial on the first floor and residential above. The pedestrian-only zone allows the commercial spaces to flow into the street creating markets, gathering areas, and patios. The residential space above densifies the area at a rate and scale that creates neighborhood character and provides customers for the commercial spaces below.
In the reimagining of the typology, additional plazas and breezeways were carved from the buildings allowing further walkability, opportunities for gathering, and more light and air to enter the interior plazas. The proposal also minimizes obstructing the view to the sea by stepping the buildings allowing for visibility while still maintaining high-density. The stepped roofs also create opportunities for roof decks and greenspace.


City Center: Portier Cove, Axonometric
![]()
Portier Cove Site History
_______________________________________________________________________________
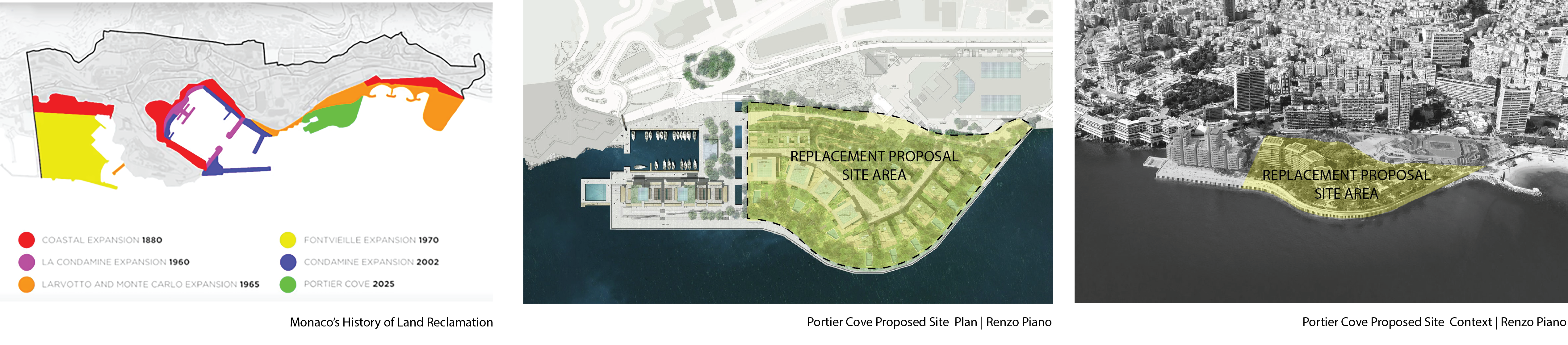
Portier Cove Site History
_______________________________________________________________________________
— AQQ