XXXXVI . Manila, Philippines
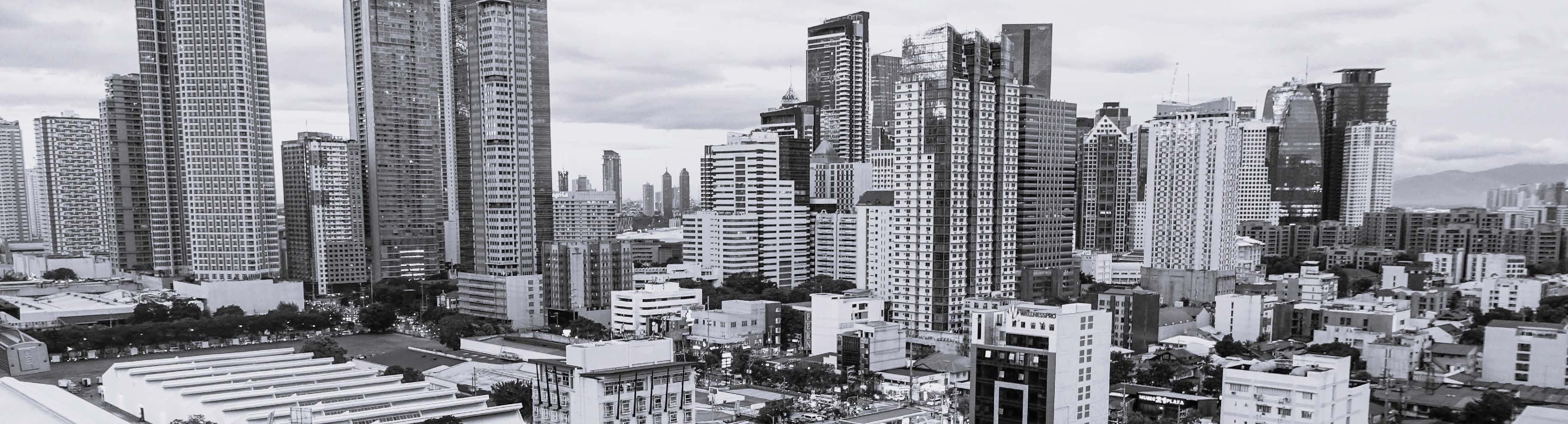

Manila, Philippines
Manila, Philippines — Mardy Hillengas
Manila is the capital city of The Philippines, with a population of ~1,847,000. In 2019 it became the most densely populated city in the world, with the 2nd and 3rd most also belonging to the Philippines.
Metro Manila has a population of around 26.7 million. The name Manila comes from a phrase meaning “where indigo is found” and the earliest evidence of human habitation dates to 3,000 B.C.E.
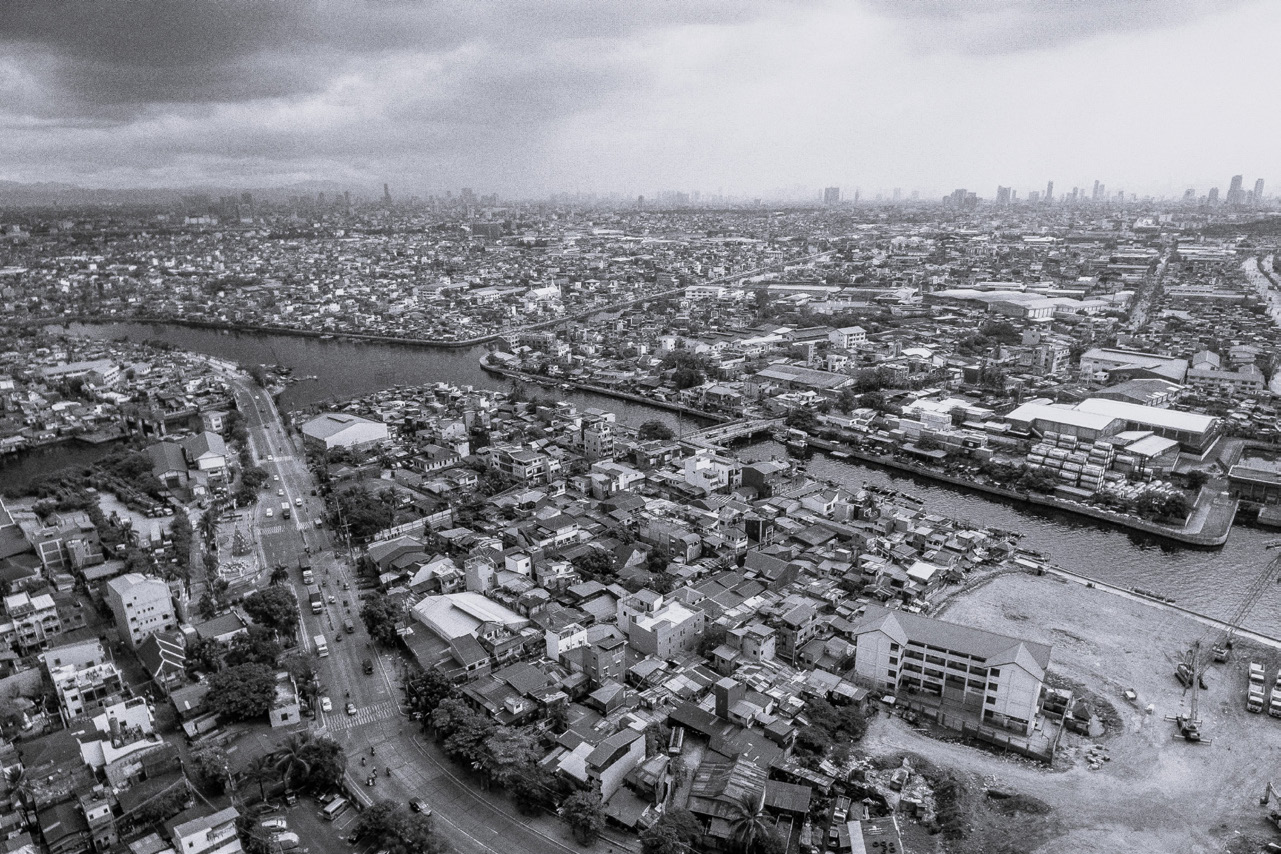


Left: Valenzuela, Metro Manila.
Right:
Mandaluyong, Metro Manila.
Urban Manila District Map:
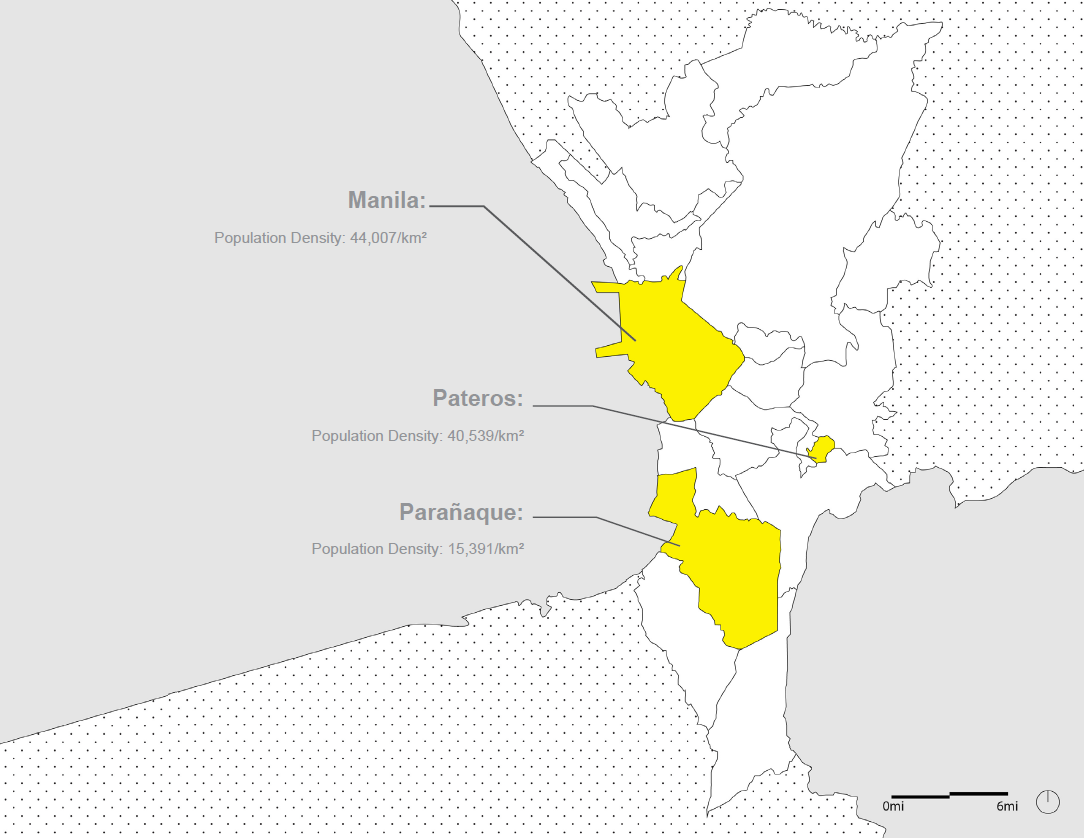
Manila, Philippines
Population:
Urban: 13,484,500 people
Metro: 1,846,500 people
Area:
Urban: 633 km2
Metro: 38 km2
Population Density:
Urban: 16,754 people/km2
Metro: 44,844 people/km2
Politics:
Being the Capital, all branches of the Philippines’ 3-branch system (legislative, executive, and judicial) are headed in Manila. Due to the Spanish and American colonial rule, the legal system is based in both Spanish civil law and American common law.
Manila proper is made up of 6 congressional districts, which are further broken up into 16 districts.
Colonization and occupation by Spain, America, and Japan has had significant influences on the political identity of Filipinos. The Philippines has almost always been highly influenced by international relations, going back to Hindu, Chinese, and Muslim traders.
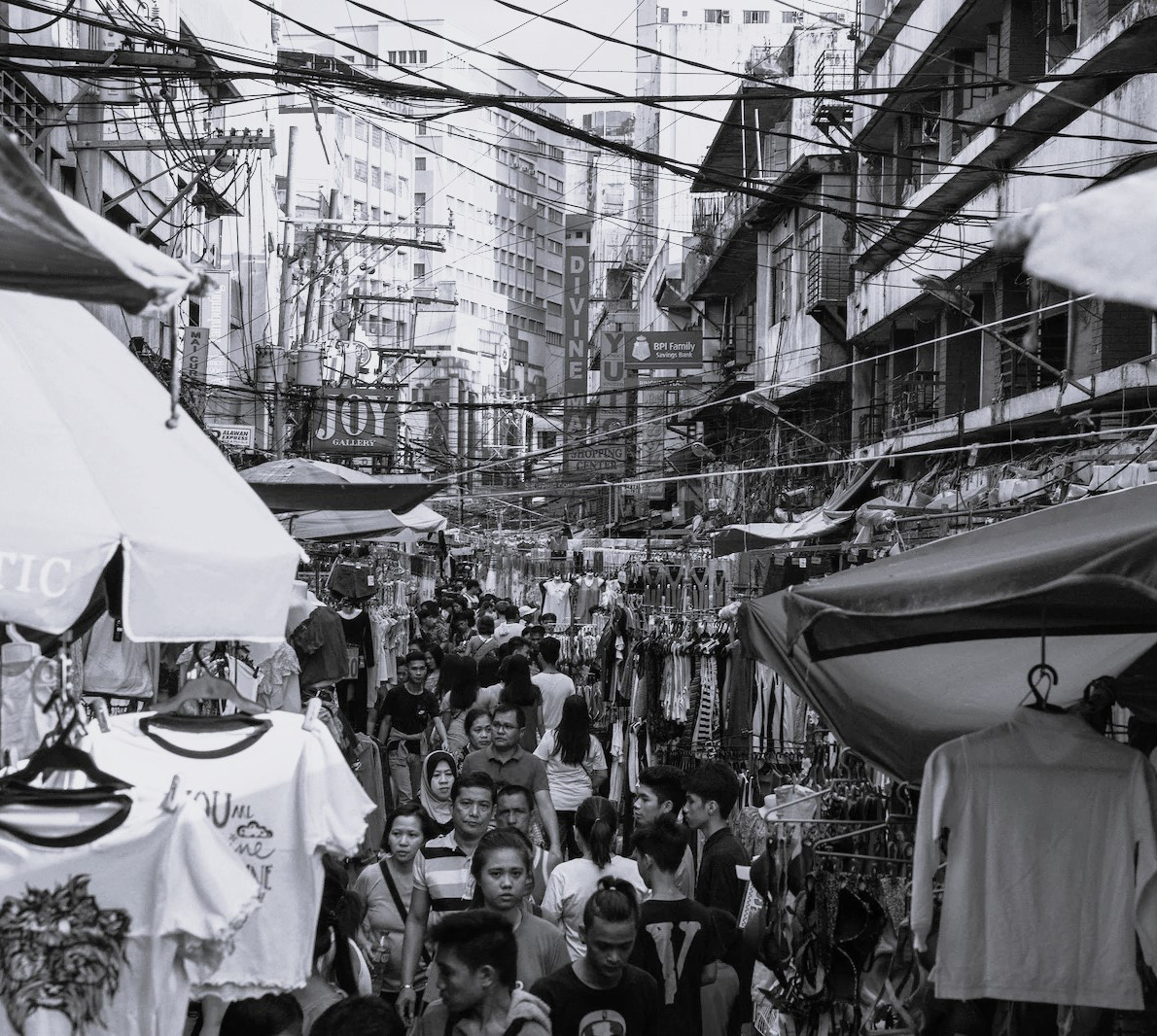
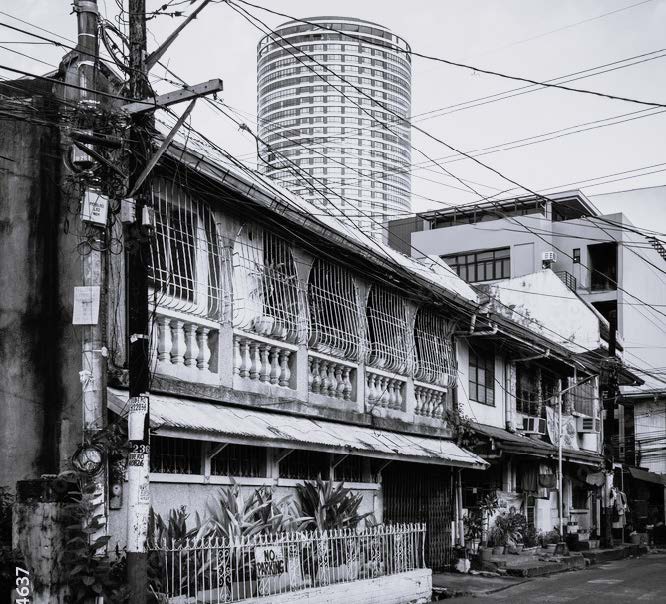
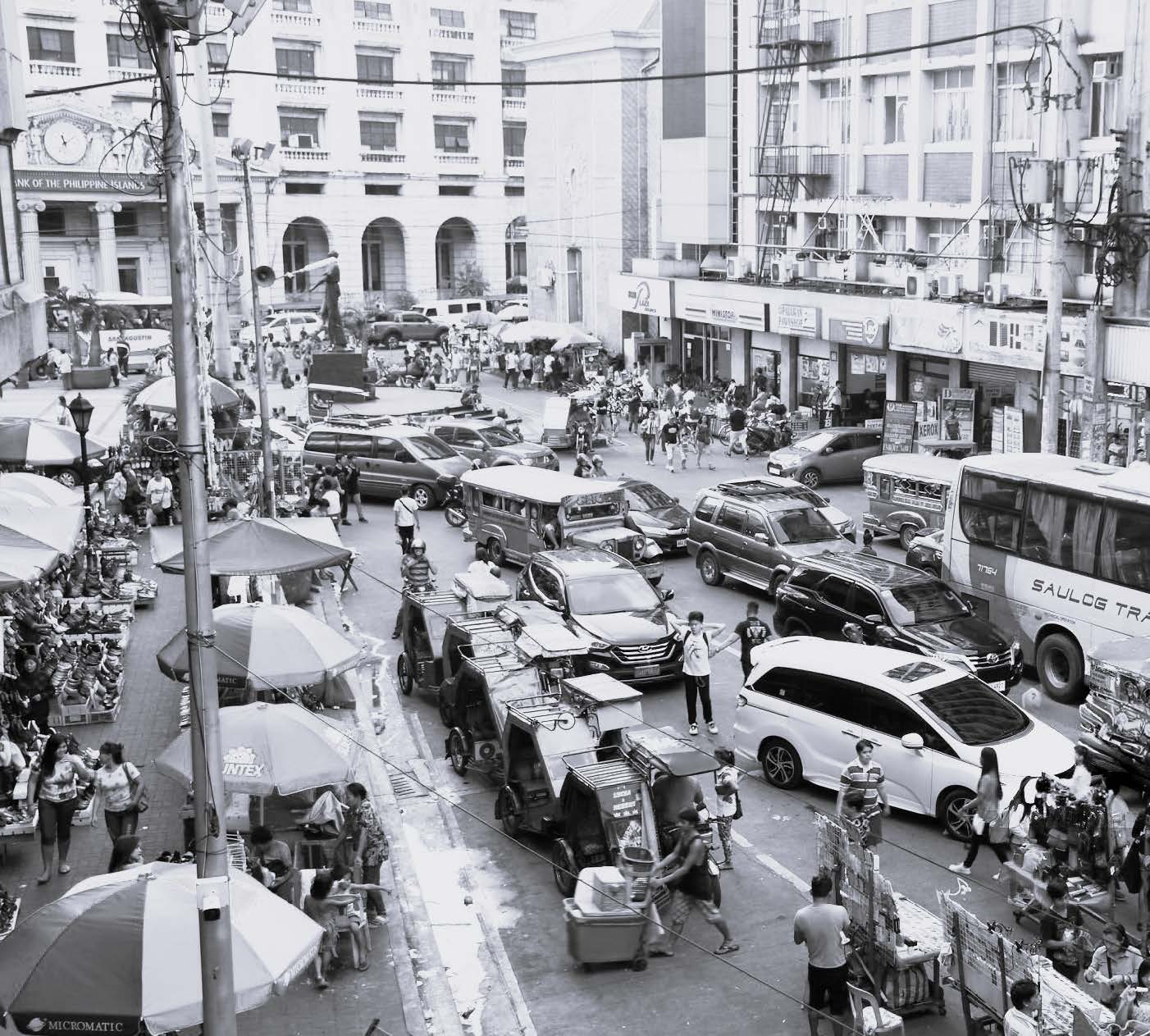




From Left to Right:
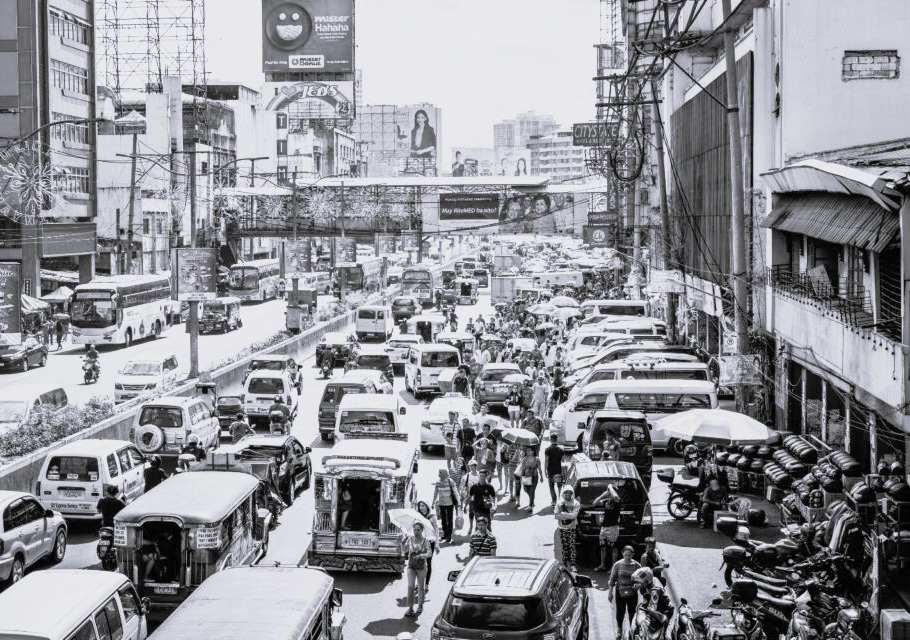
1. STREET MARKET: CROWDING DESPITE REASONABLY WIDE STREET
2. HIGH-RISE IN METRO AREA: LOW PERCEIVED DENSITY DUE TO WIDE HIGHWAY+METRO
3. STREET NEAR MAKATI: LARGE VARIATION IN HEIGHTS OF NEARBY BUILDINGS
4. COMMERCIAL STREET: EDGE OF STREET EXTENSION OF SIDEWALK
1. STREET MARKET: CROWDING DESPITE REASONABLY WIDE STREET
2. HIGH-RISE IN METRO AREA: LOW PERCEIVED DENSITY DUE TO WIDE HIGHWAY+METRO
3. STREET NEAR MAKATI: LARGE VARIATION IN HEIGHTS OF NEARBY BUILDINGS
4. COMMERCIAL STREET: EDGE OF STREET EXTENSION OF SIDEWALK
Manila, Philippines. High Density Buildig Typologies

Manila, Philippines. Urban Void Spaces

ANALYZING URBAN FABRIC
1. Tandang Sora, Quezon City:
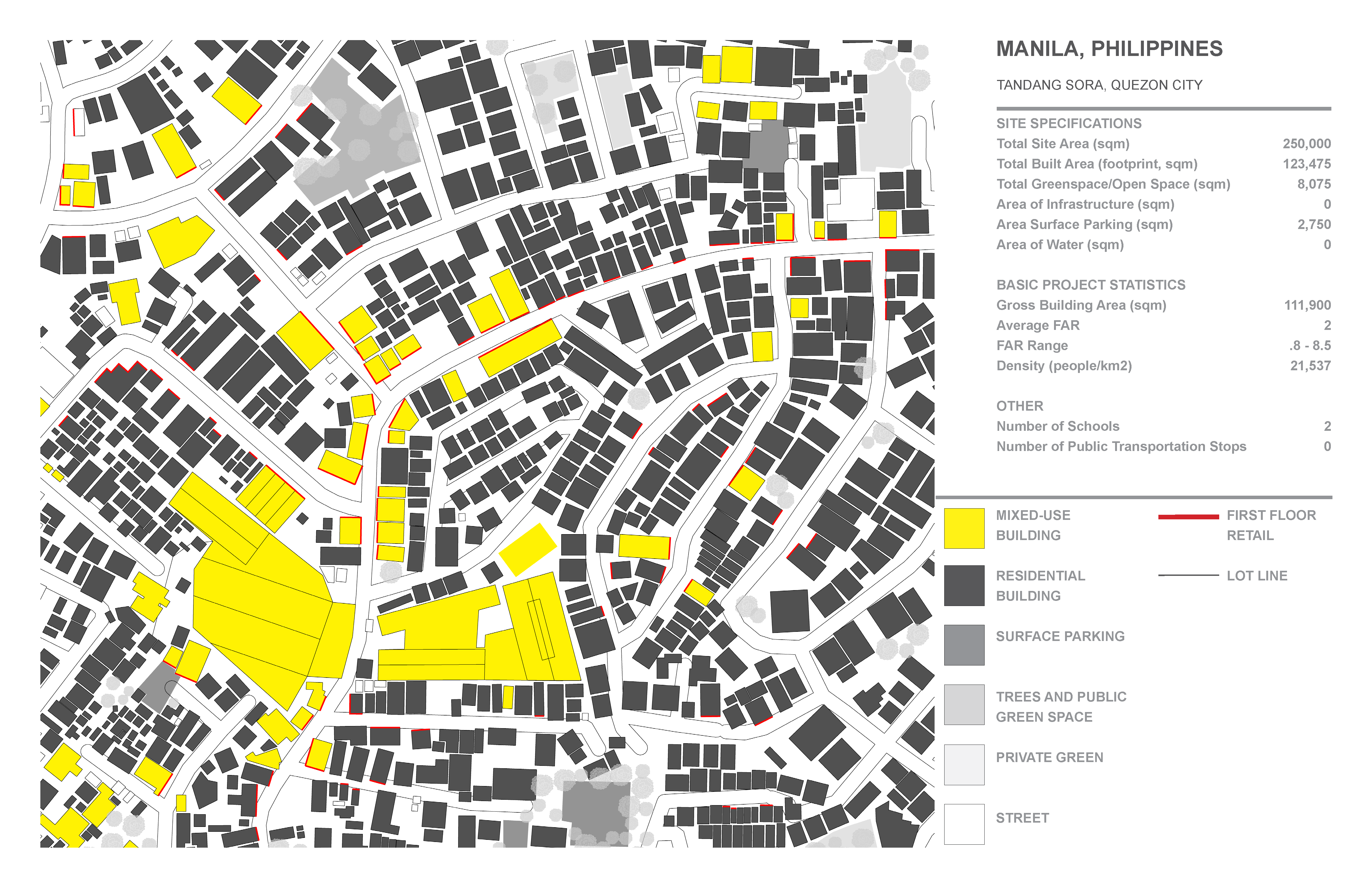

2. Poblacion, Makati:


3. Novachiles, Quezon City:


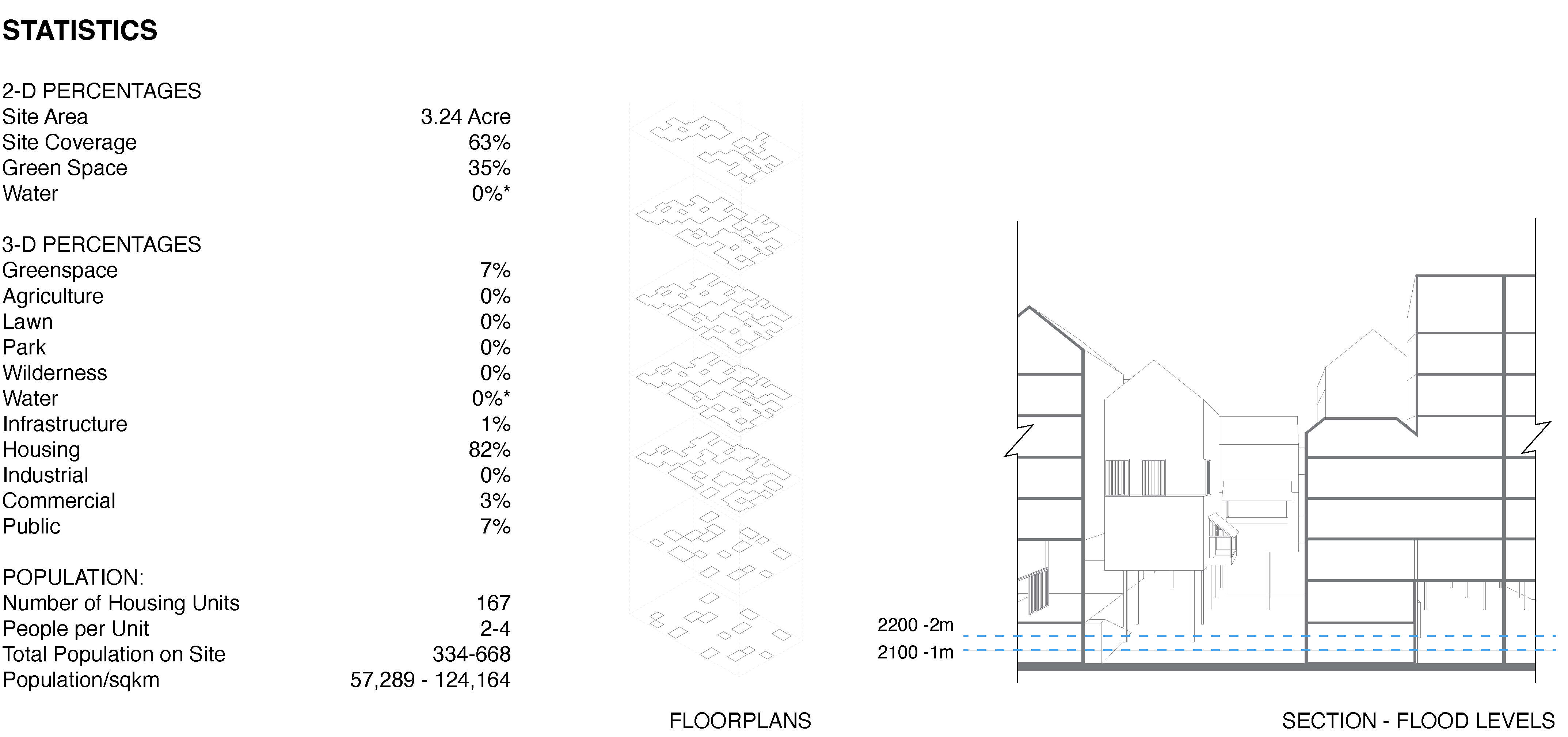
CHANGING TIDES: RESILIANCE ALONG THE PASIG, Pasig City, Manila
Located along the banks of the Pasig River in Manila, this speculative project offers a response to the challenges of urban flooding and sea level rise, both of which are acutely felt in the Philippines. Elevated on stilts, the first floor of the building takes a page from the Filipino Bahay Kubo, thereby mitigating much of the risk associated with frequent flooding. When the ground floor isn’t inundated, the ground level transforms into a dynamic public space, hosting a bustling weekend market where locals and visitors alike can gather, interact, and celebrate the city's rich heritage. Lightwells increase interior air circulation and increase light levels at ground level. Beyond mere functionality, the design prioritizes community engagement and adaptability, with expansive public patios dispersed throughout the building, equipped with sliding screens that allow occupants to customize their experience by regulating sunlight and airflow according to their preferences.
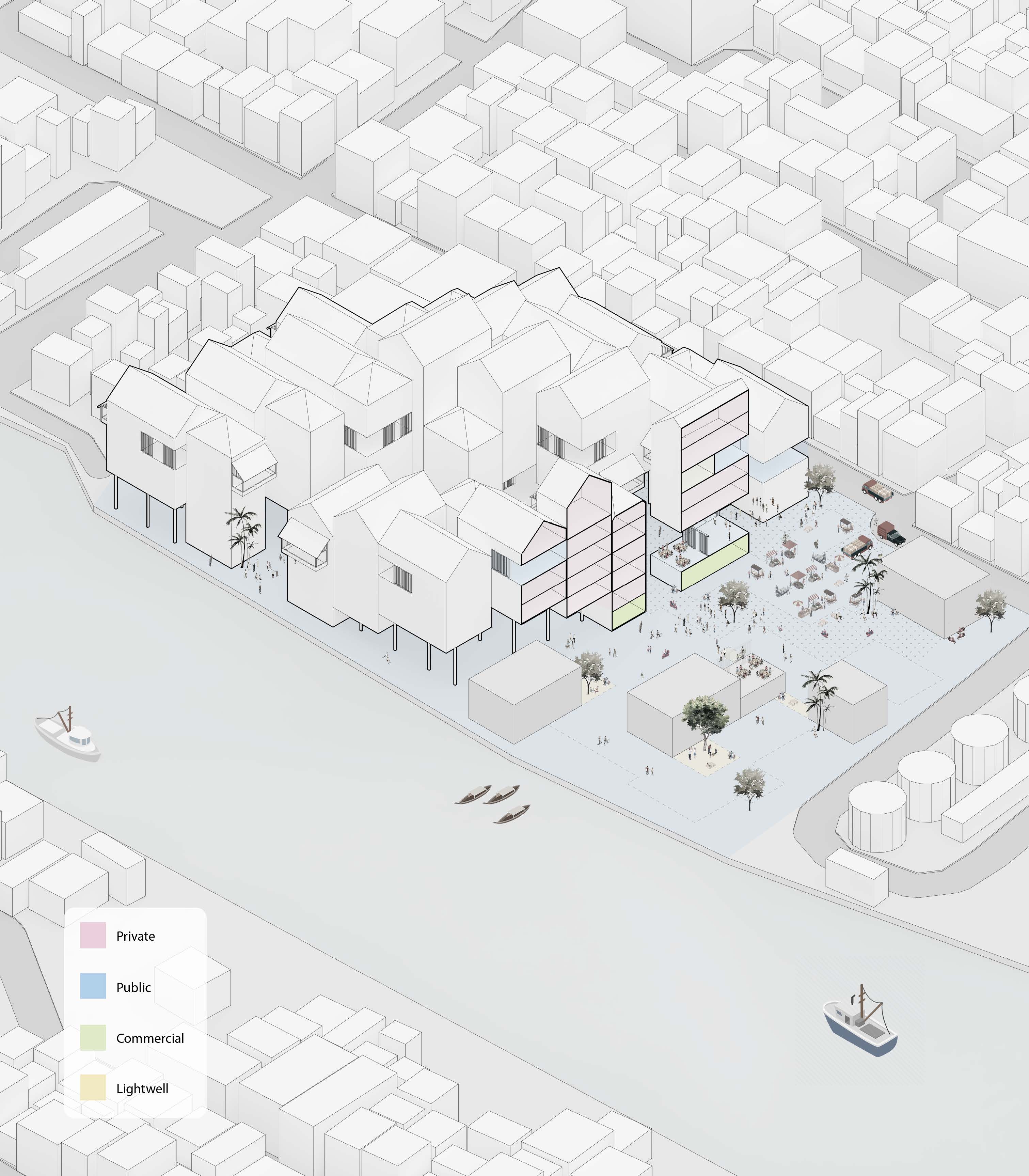 Site Plan Showing Flooding Potential
Site Plan Showing Flooding Potential
1.https://www.google.com/maps/
2.https://earth.google.com/
3.https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fWt4LMzRuFo
4.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metro_Manila
5.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manila
6.https://alphauniverse.sony-asia.com/inspire/featured/philippines-street
7.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plaza_Miranda
8.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rizal_Park
9.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/San_Agustin_Church_(Manila)
10.https://cadmapper.com/
6.https://alphauniverse.sony-asia.com/inspire/featured/philippines-street
7.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plaza_Miranda
8.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rizal_Park
9.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/San_Agustin_Church_(Manila)
12.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tandang_Sora_Avenue 13.https://www.citypopulation.de/en/philippines/quezoncity/137404120__tandang_sora/
14.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Century_City,_Makati
15.https://www.citypopulation.de/en/philippines/makati/
16.https://www.citypopulation.de/en/philippines/quezoncity/137404070__novaliches_proper/
17.https://leanurbanism.org/lean-interpretations-from-philippine-vernacular-architecture/
— AQQ